5G Network Slicing
Purpose
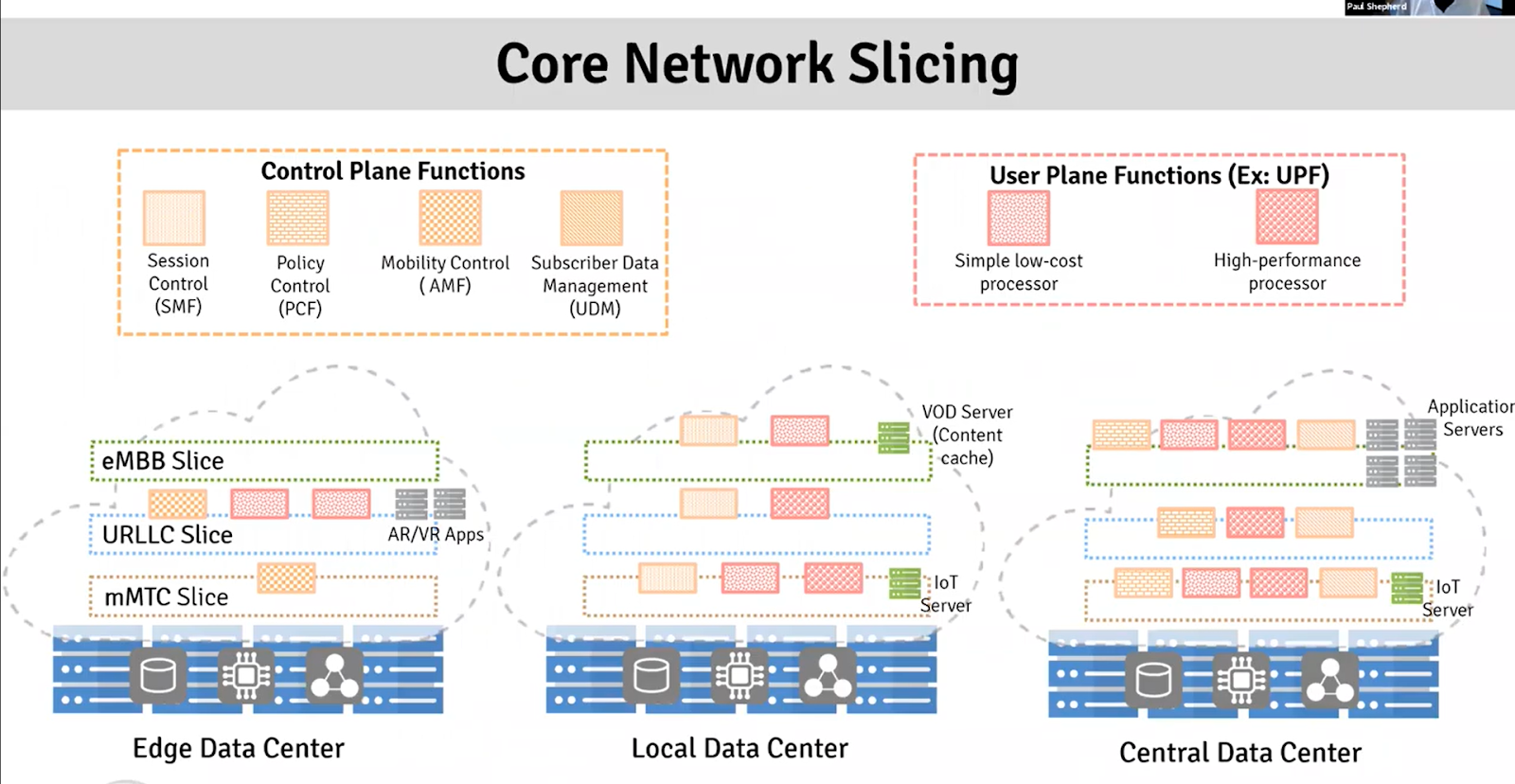
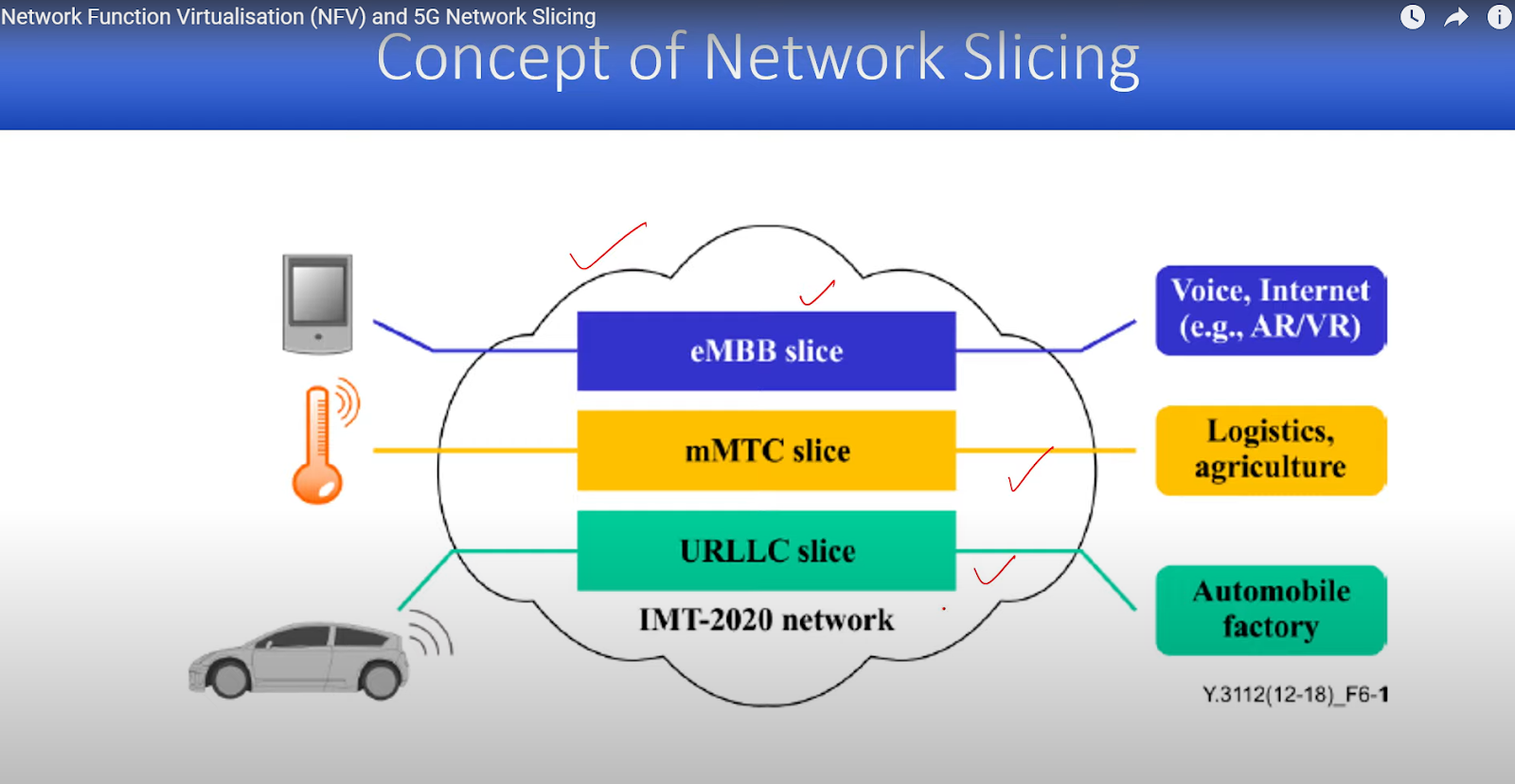
In network slicing, we consider the services we are interested in i.e., smart home, smart city, self-driving, mission-critical applications? For business models such as Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO), business vs consumers, third-party services, and CSPs services. We take a physical network and transform it into different slices. Network slicing provides suitable end-to-end QoS with optimal resource sharing. 3GPP has standardized three slices ie., mobile broadband, low latency, and massive IoT.
Network slicing require two things 1 it must have end to end 5G network , 2) we are slicing various parts of the network.
Standardized vs Non Standardized Slice
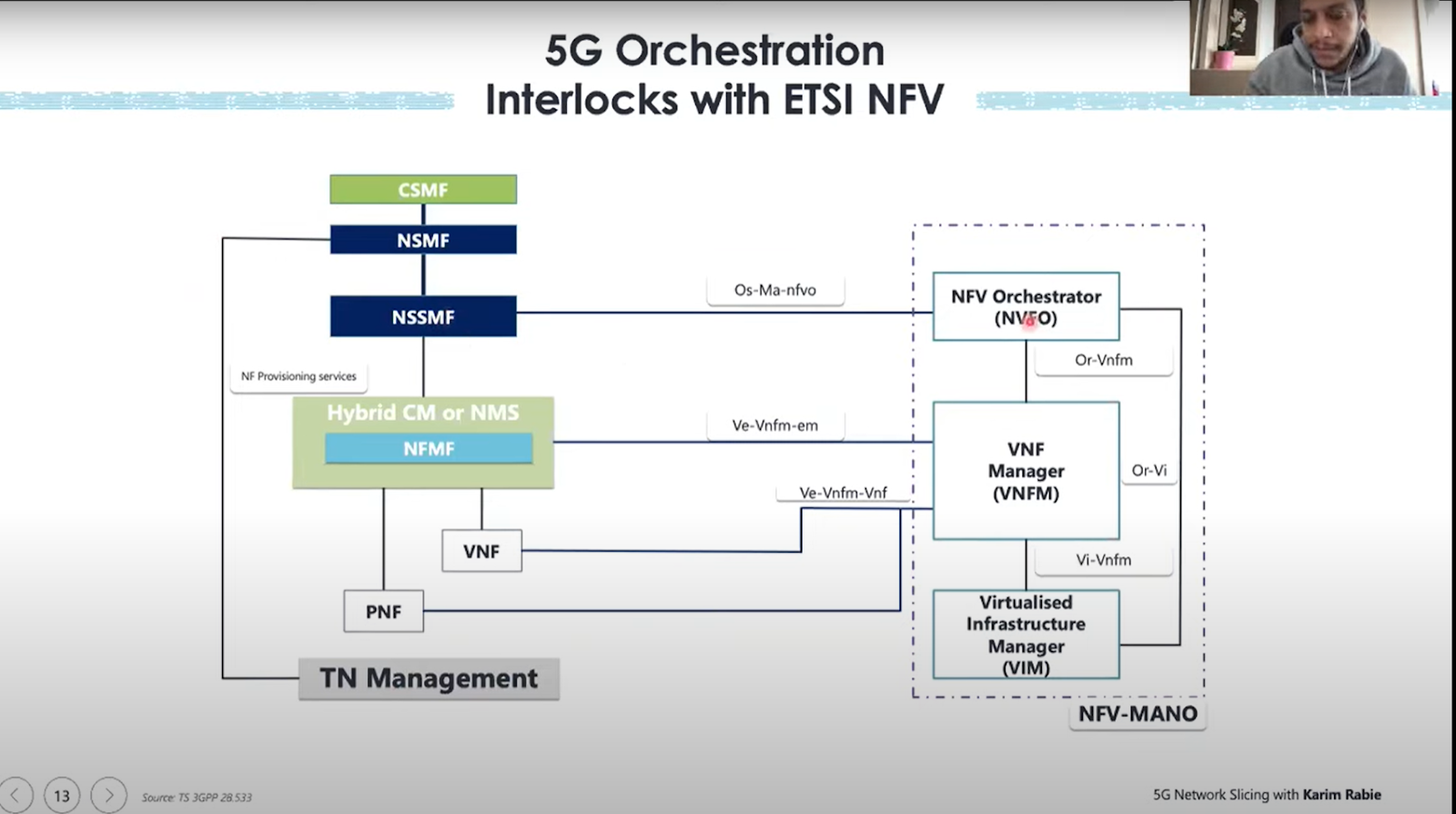
Hardware resources (compute, storage and network) are virtualized This way you can dynamically allocate resources. Above hardware there is a NFVI (network function function vierualizaed infrastructure). In the above we can deploy different virtual machines. On the right side, we have MANO part. NFV Management and Orchestration.
Each service you sell should be associated to NSI network slice instance. Each service must should be associated to NSISI. Access, Core, Transport. 3GPP is on core and access. To handle all this, we neeto have 5G orchestration framework.
ETSI NFV MANO Architecture
In 1 and 2 there are certain common functions and in network there are dedicated functions. in Access Network we have to virtualize, we can segregate, there are multiupe ways we can use to slice AN. we have to create tunnels for network slices.
The purpose of network slicing is to build a single network that could fit all. The traditional hardware and software suffer from challenges in changing network environments. For example, you may become vendor-dependent when you buy network hardware from a vendor and want to expand or change it in the future. The vendor may charge you a hefty amount even for smaller changes, updates, or improvements.
Evolution of 5G network Slicing:
We had similar technologies in 4G but not network slicing before 5G. There are many 5G usage scenarios one of them are:
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMMB) for mobile browsing.
- Ultra-reliable and low latency communication (URLLC).
- Massive Machine Type Communication (MMTC). These use cases do not require higher data rates.
Its not the optimal way to do things. Specification 23501, 23502
Network Slice Resources
- A segment of the RAN
- A segment of the Core
- A segment of the Transport Network
- One of many Services (servers)
- Suitable Lifecycle management
5G enablers
horizontal slicng is to provide based on various services URLCC, EMBB
When a user request slice AMF checks what is in the slice registration area.
Standardized vs Non Standardized Slice
RAN Slicing
Three network slices
SST (Slice Service Type)
DCN:-Dedicated core network. It was realized by virtual EPC
EPC
Charging more money is not feasible for switching from 4G to a 5G
Market PotentialNetwork Function Virtualization
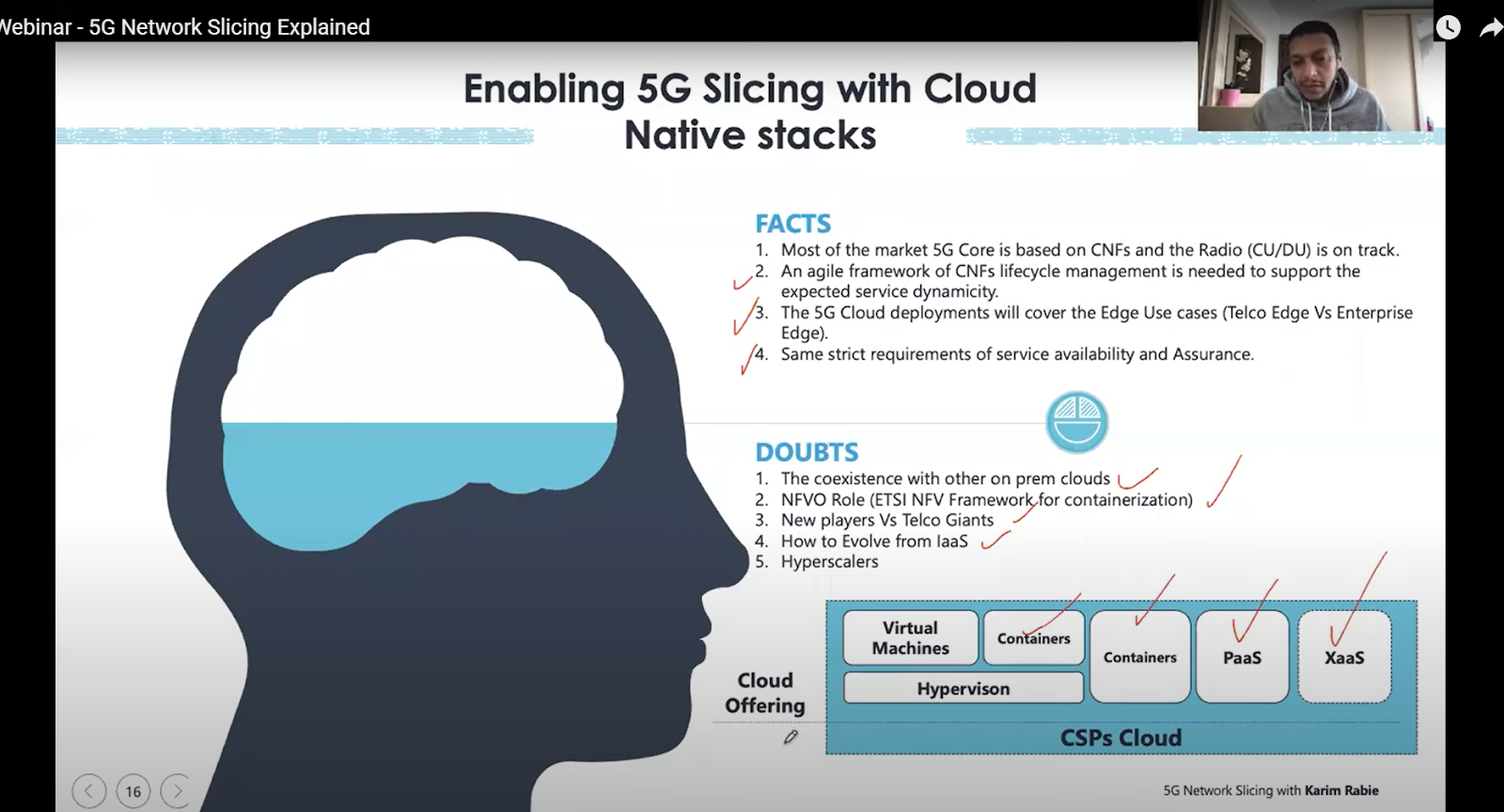
NFV comprises three components, 1). In Softwarization we have to do software on purpose-built hardware 2). Applying software functions on COTS environment 3). An orchestration that manages the software services in virtualized environments.
We can configure desirable capabilities on any hardware using NFV. However, software functions and network capacity are two different things. Network capacity includes memory, storage, etc. We can scale down easily such as at some parts the traffic is low and you can switch off some of the network instances in that area. The automatic scaling up and scaling down, the MANO can do this and we can add a rule that the traffic is this amount up or down, the MANO will control it. Docker, we create a container, and using Kubernetes we create MANO.
VM/Containers become a building block. when compute, storage and processing are virtualized and it can be deployed on containers of VMs. The au
NFV
VMs Vs Container
Infrastructure. Using any hypervisor such as VMware, or Virtualbox, we can create multiple virtual machines. Every virtual machine can have a different guest operating system. Nowadays instead of VM current world is using containers. For containers lowermost is infrastructure then we have hos operating systems will have kernel running on it, on top of it we deployed software like docker which creates a container environment, There can be different containers where containers will have different applications such as App A, App B, App C. In where VM environment, normally applications are developed by a number of developers having different machines such as windows, when the application goes to QA maybe it may not run on the QA machine, or when it goes to the customer it may not run because there are libraries required that are dependent on the machine. In a container all dependencies are part of the container kernel is on the Host Operating system and all the dependencies are on containers.
FAQs
Question 1
Is virtualization is possible between operations or is specific to one operator. Whenever you have infrastructure virtualized, there can be VNFIs there can be on VNF! Pop1, VNFI Pop2 then you can have different environments such as google cloud, azure etc
Question 2: Docker VS VMS
Docker is just for containerizing the applications. The operating system is on Host operating systems. Applications will have a small level of OS, instead for VMS, every VM has an operating system. We can event create a container on top of a VM but it will not be efficient because every VM has its own OS. Whereas like containers there will be only one OS.
Question 3:-
How many containers can be created?
There is no limit, it depends on the available hardware. If we create more containers there will be congestion.
Question 4:-
One network slice is equal to one container
No, one network slice can have n number of containers. One network can have different functions deployed on different containers.
Question 5:
Is it easy to get a license for an enterprise and build a 5G core?
It's happening in Australia, Germany, etc.
What is different between SA and NSA
SA:- when stand alone there are many requirements for 5G, standalone when we have one full end to end network. 5G RAN, 5G core, we are not relaying on LTE. between LTE and 5G, we introduce 5G RAN overall on 4G network.
SLICE REsource shared or dedicated?
Can be shared or can be dedicated depending on the deployment.
Slice preparation, creation, operation, and termination should be done based on the enterprise customers. Such as if he needs work to be done is latency-sensitive then all things should need to be taken care of.
Number of slices can go to exponentially high approx 2^32,
What happened in reality, whenever wever enterprise orders service order gives. Then a slice is initiated by CSMF/NSMF. it do service decomposition and selects the required domain i.e., NSSMF, or NSSMF transport, or NSSMF Core., and then they communicate with cloud orchestration layer.
5G Slicing Marketplace:-
A customer can come, say that he needs a 5G network slice and then uses it and they say I don't need it anymore and he/she is charged as per his/her usage.
Why Containers??
Currently, still there are VMS used. Major OEMS are set up on containers. We are able to use resources more efficiently. Faster software delivery.
A small patch of a bigger system could also be deployed. A lot of agility comes with containers.Application portability is also possible.
On websites we create ID and login one way of such application is that in the background, there is Microservices can not be created again and again. We can call these microservices. Every network function can be a microservice. So that container environment is more easier/useful in a container environment.
ETSI NFV MANO Architecture
Lopwerst is NFVI which manages virtual management resources. Onto of that VNF there we will have VNF management. On to of that There will be Network Service Managem3nt. and thenwe can connect OSS/BSS on the right side we have NFV management & Orchestration.
First layer is virtualization layer, we create virtual compute, vierutal memory, virtual network. Second layer is VNF itself, were we can create VNFs ie.e. VNF1, VNF2, VNF3. Overall management is done by VNF manager. All management is don't by VNG Manaveent and Orchestration.
physical hardware is first virtualied by virtualization software such as virtual compute, virtual memory and virtual network.
VNF manger manages lifecule management of AMF. such as modifications of network functions. which create create, modification, deletion and query.
MANO gives you flexibility in deployment and testing. The container uses the host operating system, we can import a container from wherever it has been developed its like copy and pasting, for VM we have to install the software and check whether it's working or not. Facebook, Google, and Netflix use containers. The management part of the c dot is Kubernetes. Kubernetes was owned by Google and now they don't it open source. Telecome infrastructure is virtualized and deployed
Top part is the orchestration. All managements are done by orchestration part. Once we have virtualized the network, it becomes easy for the operator to If we create AMF, it will have a networking involved, lets say we create network function such as AMF, we will need to have IP address, altohgout we created a network function but we have not given IP and other resources. It has not been advertised throughout the network.
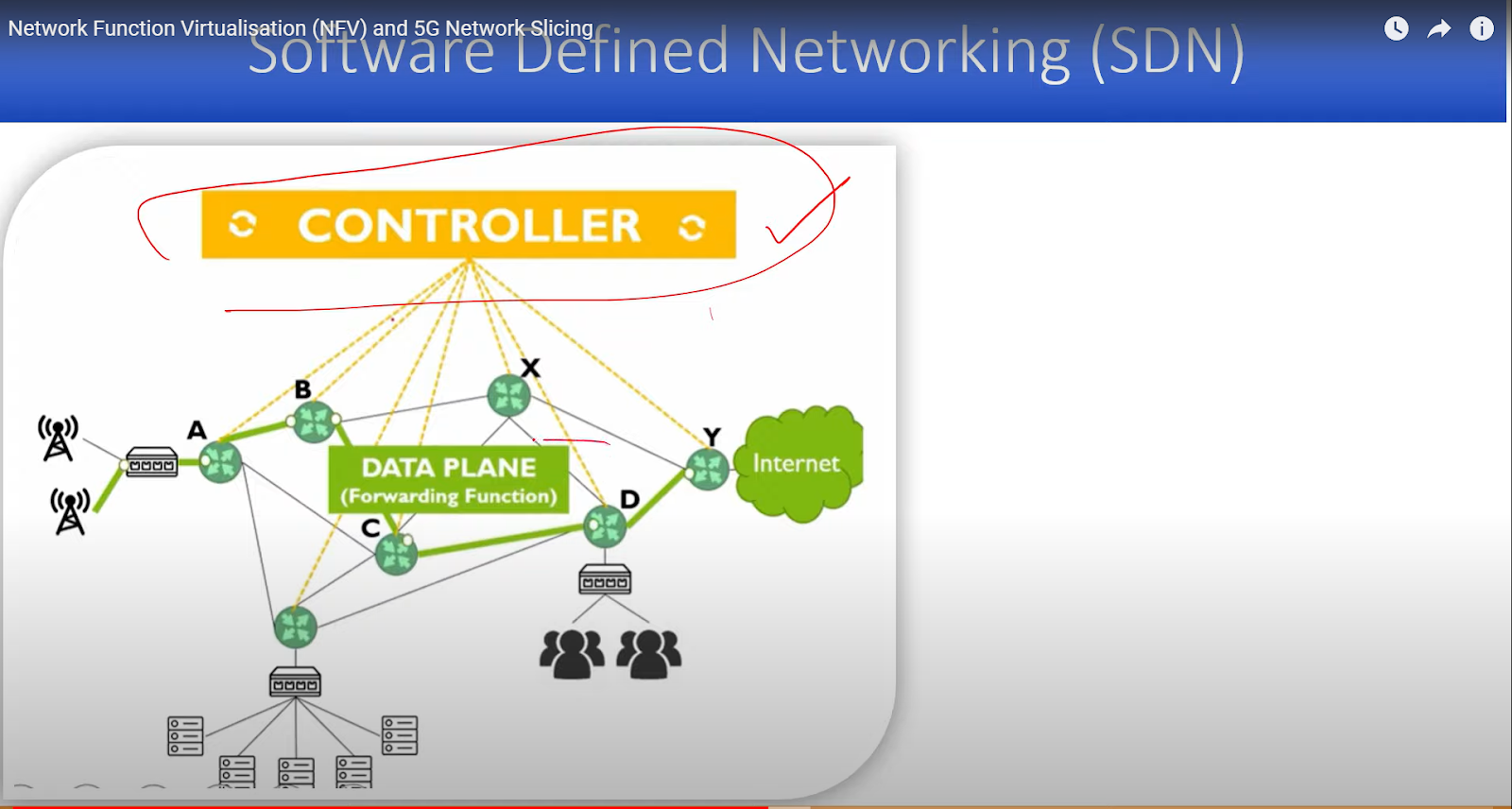
In traditional networks, we can see there are different routers. In these networks the control part is in the network elements such as IP addresses. etc.
At this stage comes SDN. We separate user plane and control plane. Along with NFV, we can also program. Control and data forwarding planes are sepate view. There will be a separate view.
ETSI MANO:- It's the right side of the NFV. Open Source MANO OSM Release TEN.
3GPP standard of IT is that,
MANO gives you flexibility in deployment and testing. The container uses the host operating system, we can import a container from wherever it has been developed its like copy and pasting, for VM we have to install the software and check whether it's working or not. Facebook, Google, and Netflix use containers. The management part of the c dot is Kubernetes. Kubernetes was owned by Google and now they don't it open source. Telecome infrastructure is virtualized and deployed
5G Network Slicing
How NFV is important in network slicing. Network slicing allows the services provider to create multiple logical networks over the same physical infrastructure.
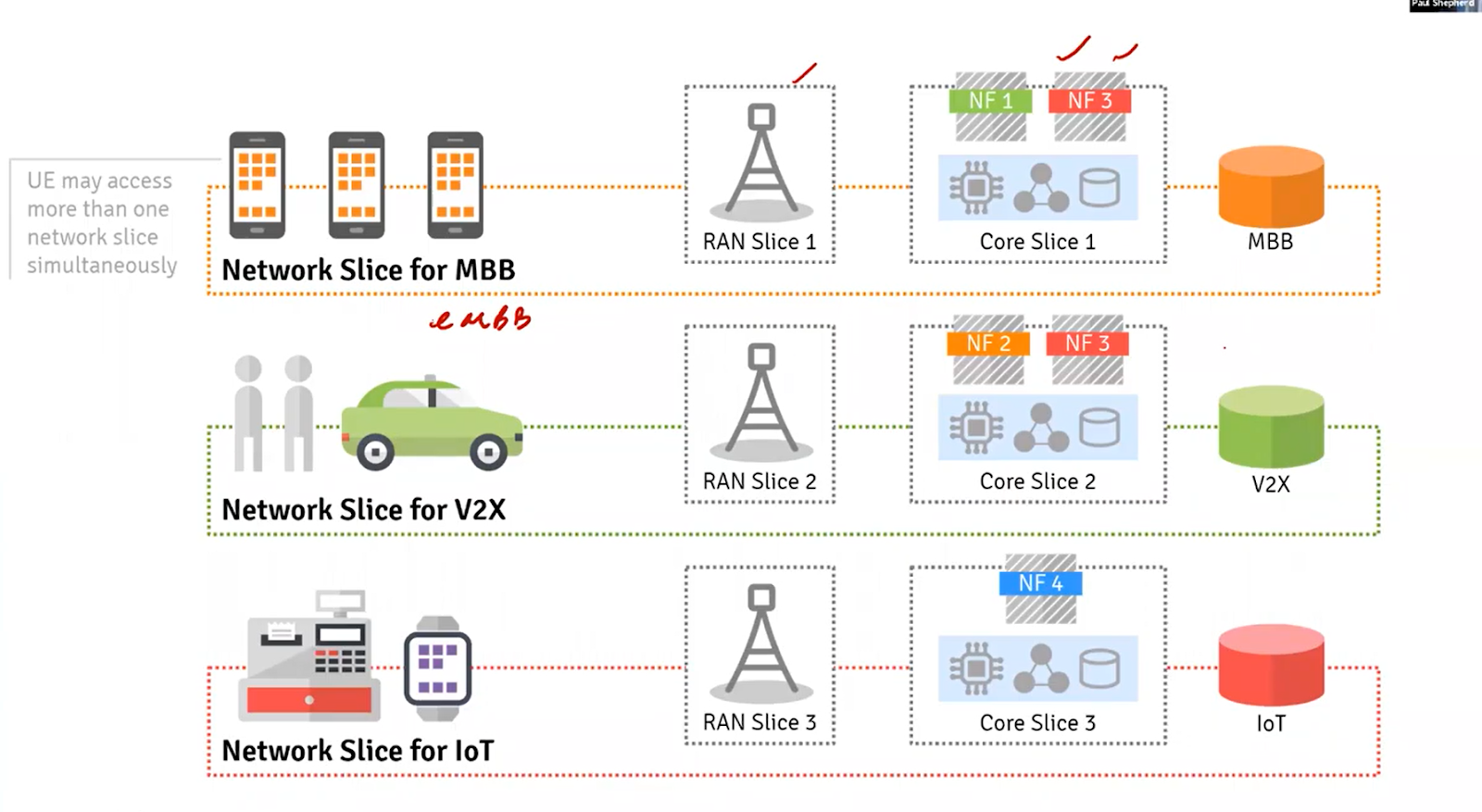
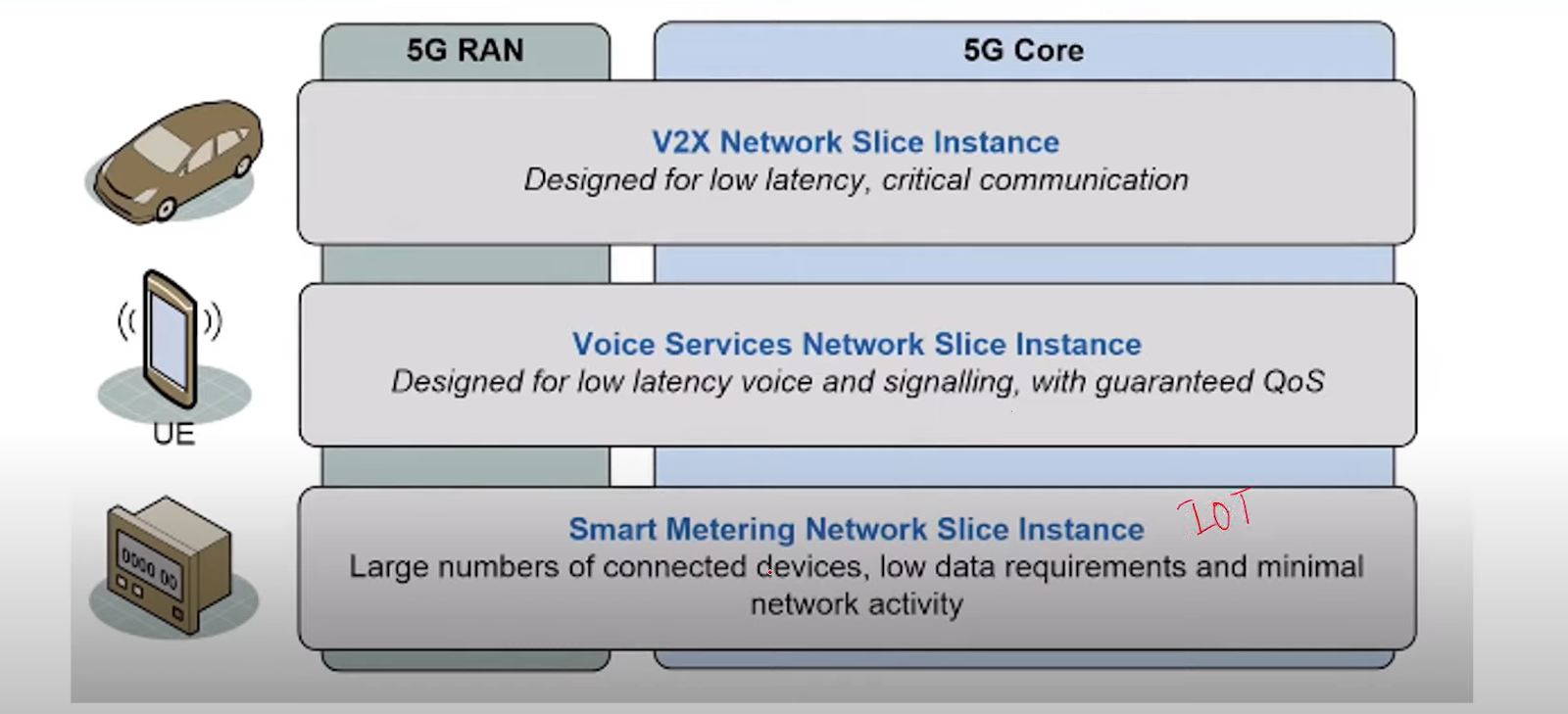
For example in the above application we can have one slice for V2X network. 3GPP has defined can access up to 8 network slices. On the number of slices, there is no limit defined. In the following example V2X need URLLC need to have URLLC and eMBB slice. At the network live there are two slices such as eMBB Slice, uRLLC_ A Motoer Slice, uRLLC_B mother Slice, IMT-2020 network however, at the service level there is one slice.
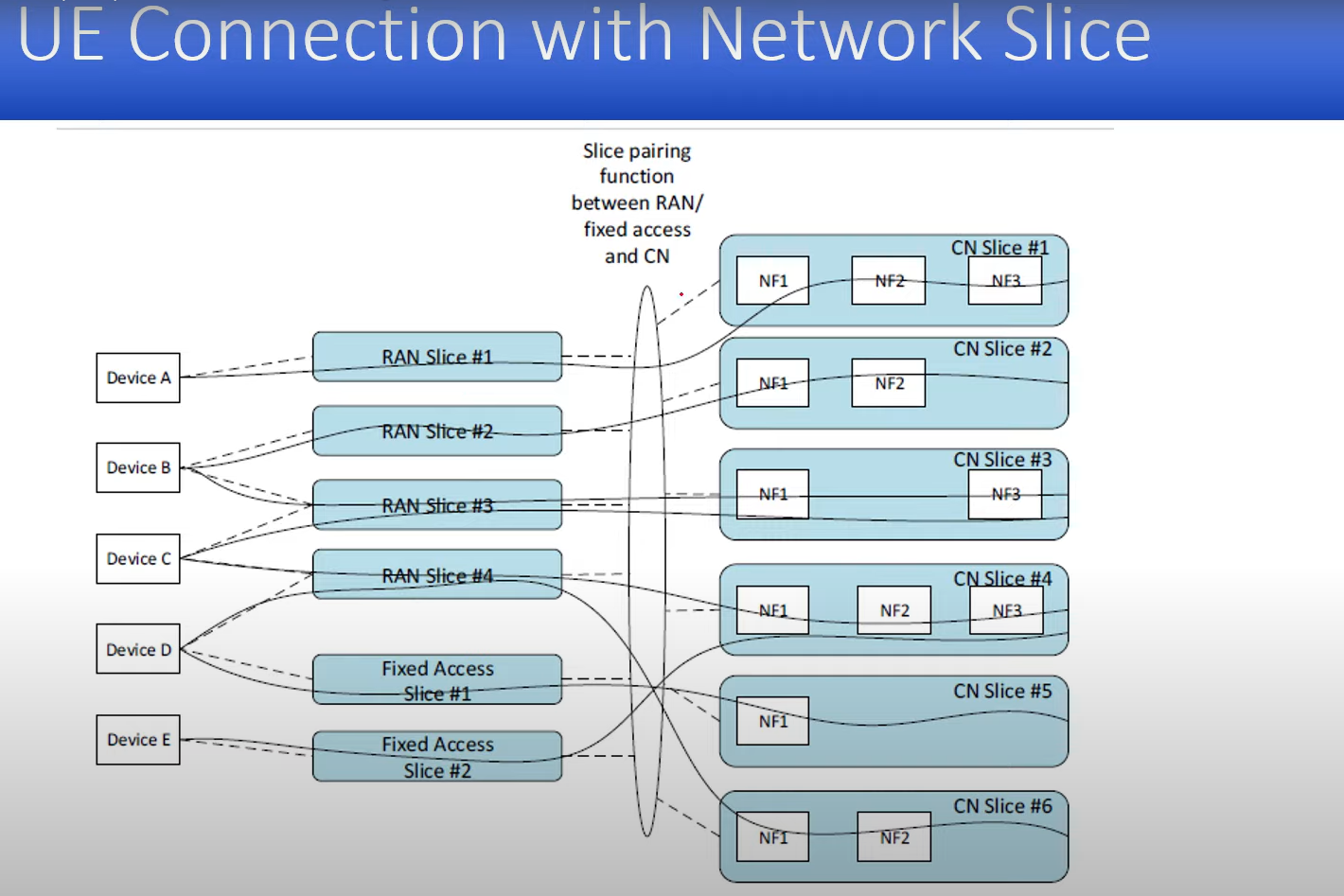
UE can have access to multiple network slices.
4GPP Network Slicing
UE can have access to multiple network slices.
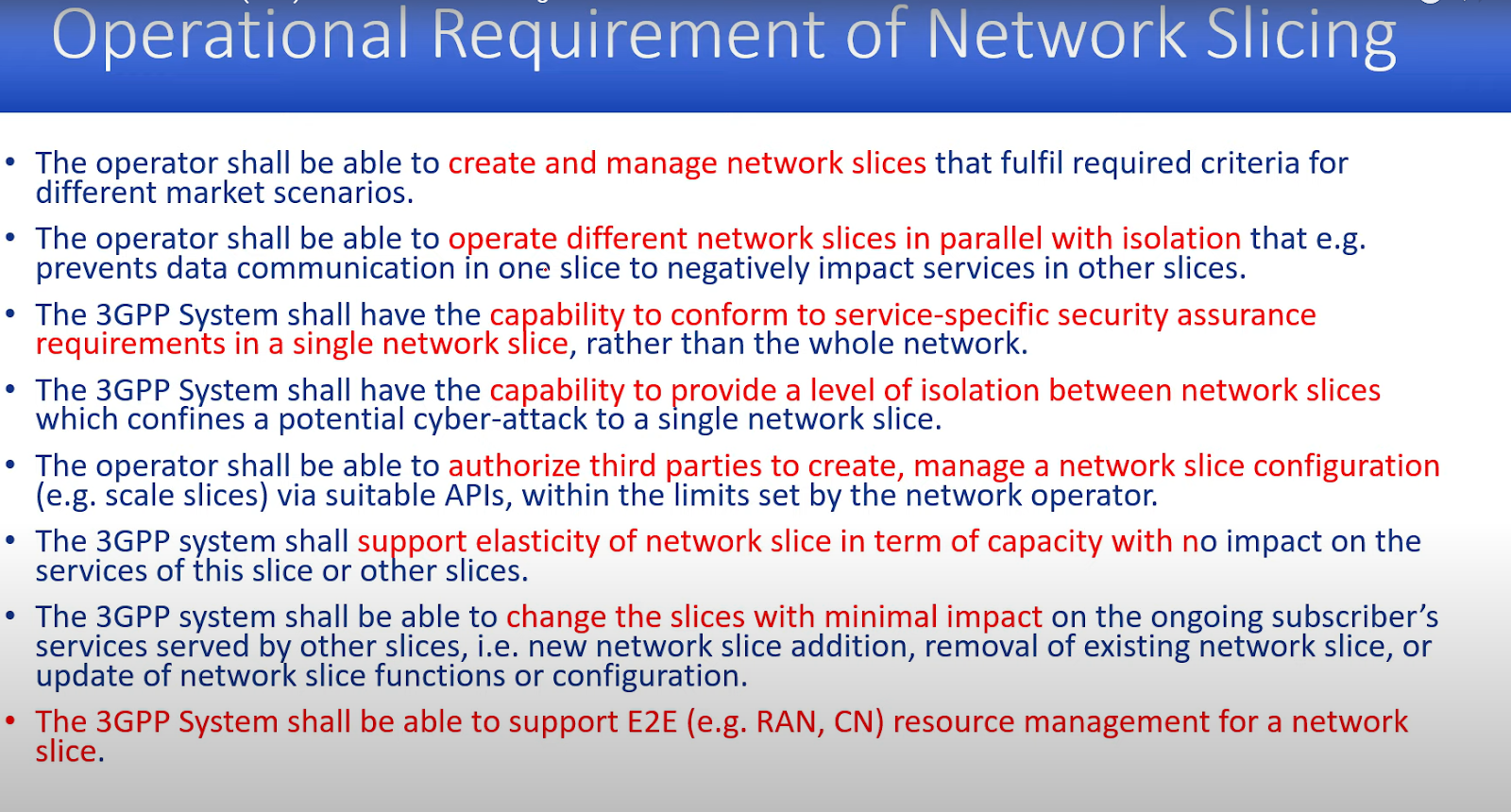
3GPP release 13 they released a document after feasibility study in that document, they had talked about certain requirements of network slicing.
Operator Requirements
4GPP Network Slicing
In the following image there are three slices are connected to data networks. The have dedicated SMF< PCF, however, NRF, PCF, and AMF is comment to slice 1 and slice. So there are some common functions and some are shared.
In 1 and 2 there are certain common functions and in network there are dedicated functions. in Access Network we have to virtualize, we can segregate, there are multiupe ways we can use to slice AN. we have to create tunnels for network slices.
GCMA networking white paper.
MANO will create service instance



































Comments
Post a Comment